「App:Library:LVGL:docs:Overview:Objects」の版間の差分
| 29行目: | 29行目: | ||
You can set/get these attributes with <code>lv_obj_set_...</code> and <code>lv_obj_get_...</code> functions. For example: | You can set/get these attributes with <code>lv_obj_set_...</code> and <code>lv_obj_get_...</code> functions. For example: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="C++" style="border: 1px dashed gray;"> | ||
/*Set basic object attributes*/ | /*Set basic object attributes*/ | ||
lv_obj_set_size(btn1, 100, 50); /*Set a button's size*/ | lv_obj_set_size(btn1, 100, 50); /*Set a button's size*/ | ||
lv_obj_set_pos(btn1, 20,30); /*Set a button's position*/ | lv_obj_set_pos(btn1, 20,30); /*Set a button's position*/ | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
To see all the available functions visit the Base object's documentation. | To see all the available functions visit the Base object's documentation. | ||
| 41行目: | 43行目: | ||
For these special attributes, every object type may have unique API functions. For example for a slider: | For these special attributes, every object type may have unique API functions. For example for a slider: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="C++" style="border: 1px dashed gray;"> | ||
/*Set slider specific attributes*/ | /*Set slider specific attributes*/ | ||
lv_slider_set_range(slider1, 0, 100); /*Set the min. and max. values*/ | lv_slider_set_range(slider1, 0, 100); /*Set the min. and max. values*/ | ||
lv_slider_set_value(slider1, 40, LV_ANIM_ON); /*Set the current value (position)*/ | lv_slider_set_value(slider1, 40, LV_ANIM_ON); /*Set the current value (position)*/ | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
The API of the widgets is described in their Documentation but you can also check the respective header files (e.g. ''widgets/lv_slider.h'') | The API of the widgets is described in their Documentation but you can also check the respective header files (e.g. ''widgets/lv_slider.h'') | ||
| 53行目: | 59行目: | ||
=== Moving together === | === Moving together === | ||
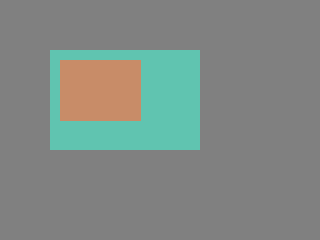
If the position of a parent changes, the children will move along with it. Therefore, all positions are relative to the parent. | If the position of a parent changes, the children will move along with it. Therefore, all positions are relative to the parent. | ||
| + | |||
[[file:LVGL docs overview objects 01.png|link=https://docs.lvgl.io/8.2/overview/object.html]] | [[file:LVGL docs overview objects 01.png|link=https://docs.lvgl.io/8.2/overview/object.html]] | ||
| + | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="C++" style="border: 1px dashed gray;"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="C++" style="border: 1px dashed gray;"> | ||
lv_obj_t * parent = lv_obj_create(lv_scr_act()); /*Create a parent object on the current screen*/ | lv_obj_t * parent = lv_obj_create(lv_scr_act()); /*Create a parent object on the current screen*/ | ||
| 61行目: | 69行目: | ||
lv_obj_set_pos(obj1, 10, 10); /*Set the position of the new object*/ | lv_obj_set_pos(obj1, 10, 10); /*Set the position of the new object*/ | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
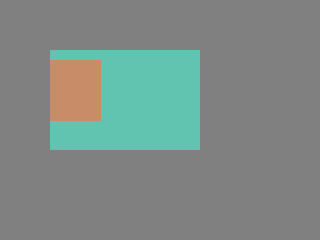
Modify the position of the parent: | Modify the position of the parent: | ||
| + | |||
[[file:LVGL docs overview objects 02.png|link=https://docs.lvgl.io/8.2/overview/object.html]] | [[file:LVGL docs overview objects 02.png|link=https://docs.lvgl.io/8.2/overview/object.html]] | ||
| + | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="C++" style="border: 1px dashed gray;"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="C++" style="border: 1px dashed gray;"> | ||
lv_obj_set_pos(parent, 50, 50); /*Move the parent. The child will move with it.*/ | lv_obj_set_pos(parent, 50, 50); /*Move the parent. The child will move with it.*/ | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
(For simplicity the adjusting of colors of the objects is not shown in the example.) | (For simplicity the adjusting of colors of the objects is not shown in the example.) | ||
Visibility only on the parent | Visibility only on the parent | ||
If a child is partially or fully outside its parent then the parts outside will not be visible. | If a child is partially or fully outside its parent then the parts outside will not be visible. | ||
| + | |||
[[file:LVGL docs overview objects 03.png|link=https://docs.lvgl.io/8.2/overview/object.html]] | [[file:LVGL docs overview objects 03.png|link=https://docs.lvgl.io/8.2/overview/object.html]] | ||
| + | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="C++" style="border: 1px dashed gray;"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="C++" style="border: 1px dashed gray;"> | ||
lv_obj_set_x(obj1, -30); /*Move the child a little bit off the parent*/ | lv_obj_set_x(obj1, -30); /*Move the child a little bit off the parent*/ | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
:[[App:Library:LVGL:docs:Overview|戻る : Previous]] | :[[App:Library:LVGL:docs:Overview|戻る : Previous]] | ||
2022年6月22日 (水) 23:09時点における版
https://docs.lvgl.io/8.2/overview/object.html
| 英文 | 自動翻訳 |
|---|---|
Objects
In LVGL the basic building blocks of a user interface are the objects, also called Widgets. For example a Button, Label, Image, List, Chart or Text area.
You can see all the Object types here.
All objects are referenced using an lv_obj_t pointer as a handle. This pointer can later be used to set or get the attributes of the object.
Attributes
Basic attributes
All object types share some basic attributes:
- Position
- Size
- Parent
- Styles
- Event handlers
- Etc
You can set/get these attributes with lv_obj_set_... and lv_obj_get_... functions. For example:
/*Set basic object attributes*/
lv_obj_set_size(btn1, 100, 50); /*Set a button's size*/
lv_obj_set_pos(btn1, 20,30); /*Set a button's position*/
To see all the available functions visit the Base object's documentation.
Specific attributes
The object types have special attributes too. For example, a slider has
- Minimum and maximum values
- Current value
For these special attributes, every object type may have unique API functions. For example for a slider:
/*Set slider specific attributes*/
lv_slider_set_range(slider1, 0, 100); /*Set the min. and max. values*/
lv_slider_set_value(slider1, 40, LV_ANIM_ON); /*Set the current value (position)*/
The API of the widgets is described in their Documentation but you can also check the respective header files (e.g. widgets/lv_slider.h)
Working mechanisms
Parent-child structure
A parent object can be considered as the container of its children. Every object has exactly one parent object (except screens), but a parent can have any number of children. There is no limitation for the type of the parent but there are objects which are typically a parent (e.g. button) or a child (e.g. label).
Moving together
If the position of a parent changes, the children will move along with it. Therefore, all positions are relative to the parent.
lv_obj_t * parent = lv_obj_create(lv_scr_act()); /*Create a parent object on the current screen*/
lv_obj_set_size(parent, 100, 80); /*Set the size of the parent*/
lv_obj_t * obj1 = lv_obj_create(parent); /*Create an object on the previously created parent object*/
lv_obj_set_pos(obj1, 10, 10); /*Set the position of the new object*/
Modify the position of the parent:
lv_obj_set_pos(parent, 50, 50); /*Move the parent. The child will move with it.*/
(For simplicity the adjusting of colors of the objects is not shown in the example.)
Visibility only on the parent If a child is partially or fully outside its parent then the parts outside will not be visible.
lv_obj_set_x(obj1, -30); /*Move the child a little bit off the parent*/